Understanding Human Development In North America: A Color-Coded Perspective
Human development is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various factors influencing the overall well-being of individuals and communities. In recent years, researchers and policymakers have used color-coded systems to represent different levels of human development across regions. For instance, in many graphs and maps, the color red often signifies low human development, while other colors represent moderate to high levels. When we examine North America, we find a complex tapestry of human development indicators, revealing both strengths and weaknesses that contribute to the region's overall socio-economic landscape.
In understanding the dynamics of moderate human development, red = low human development, North America and its diverse populations, it's imperative to consider various indicators like education, income, health, and access to resources. These indicators help paint a clearer picture of where certain areas stand in terms of human development. The implications of these statistics are far-reaching, affecting everything from policy-making to community planning and international relations.
As we delve deeper into the subject, we will explore the factors that contribute to moderate human development, the challenges posed by low human development areas marked in red, and the unique context of North America. By examining these elements, we can gain insights into how different regions can foster growth and improve the quality of life for their inhabitants.
What is Human Development?
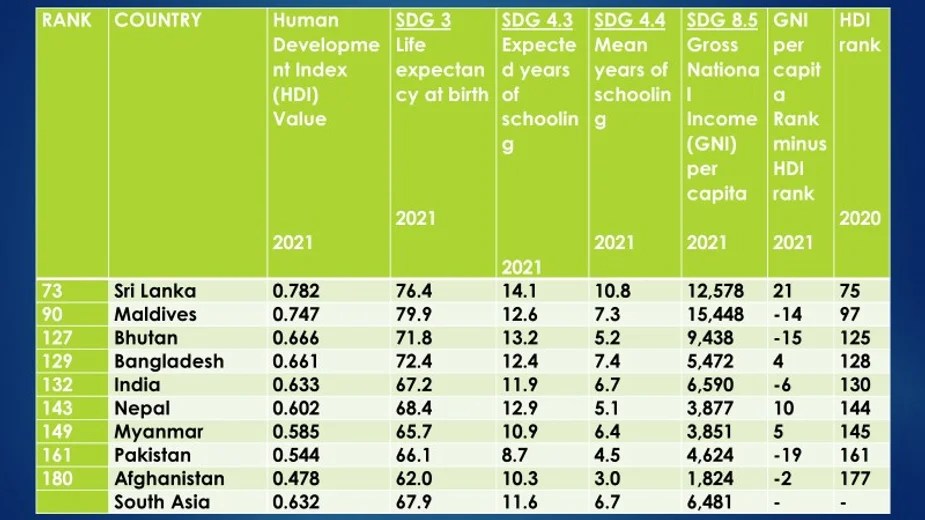
Human development is a concept that goes beyond mere economic growth, focusing on the enhancement of the quality of life and well-being of individuals. It takes into account various dimensions such as education, health, and income. The Human Development Index (HDI) is a prominent measure used to assess human development levels across different countries and regions.
How is Human Development Measured?
The measurement of human development involves several key indicators:
- Life expectancy at birth
- Educational attainment (average years of schooling)
- Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
These indicators are combined to produce the HDI, which categorizes countries and regions into different levels of human development, ranging from low to very high.
What Does Moderate Human Development Mean?
Moderate human development refers to regions that exhibit a balance of educational, health, and economic indicators. These areas often have access to essential services and opportunities but may still face certain challenges that prevent them from achieving high human development status. In North America, some areas may be classified as having moderate human development due to disparities in resource distribution, economic opportunities, or educational access.
What Are the Implications of Low Human Development in North America?
Areas marked in red, indicative of low human development, face numerous challenges that can hinder growth and overall quality of life. These challenges often include:
- High unemployment rates
- Lack of access to quality education
- Poor health services and outcomes
- Increased poverty levels
Such conditions can create a cycle of disadvantage, making it difficult for communities to break free from low human development status.
How Can Communities Improve Human Development?
Improving human development requires targeted efforts at various levels. Communities can take several approaches to enhance their development status, including:
- Investing in education and vocational training
- Improving healthcare access and quality
- Encouraging economic development through job creation
- Fostering community engagement and participation in decision-making
By focusing on these areas, communities can work towards improving their overall human development status.
What Role Does Government Policy Play in Human Development?
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of human development. Effective policies can lead to improved access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Governments can implement programs aimed at:
- Reducing income inequality
- Enhancing public services
- Promoting inclusive economic growth
By prioritizing human development in policy-making, governments can create environments that foster growth and improve quality of life for all citizens.
How Does North America Compare to Other Regions in Terms of Human Development?
North America, as a region, generally enjoys a higher level of human development compared to many parts of the world. However, disparities exist within the region. Some areas, particularly rural or economically disadvantaged regions, may exhibit low human development indicators, reflected by the color red on various maps and charts. This comparison highlights the need for continuous efforts to address inequalities within the region.
What Future Trends Can We Expect in Human Development in North America?
Looking ahead, several trends may influence human development in North America:
- Increased focus on sustainable development
- Technological advancements improving access to education and healthcare
- Greater emphasis on social equity and inclusion
These trends hold the potential to enhance human development outcomes and reduce the prevalence of areas marked by low human development.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Human Development in North America
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of moderate human development, red = low human development, North America and its implications is vital for fostering growth and improving quality of life. By addressing the challenges faced by low human development areas and implementing effective strategies at the community and government levels, North America can continue to progress towards a more equitable and prosperous future for all its residents.

ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6mpp2dopbBpnnHrqSapl2Zsrexy6inpp2eqXqzscNmo6ivXZ3Crq3NZpuerpWhvLG5xKerZqafp8GpecCmnKuhk5Z6orrDZ5%2BtpZw%3D