How Continents And Glaciers Shaped Our World
Throughout the ages, our planet has undergone profound transformations, largely driven by the movement of continents and the relentless advance of glaciers. These colossal forces of nature have not only sculpted the physical landscape but have also influenced the climate, ecosystems, and even human civilizations. Understanding how they have impacted our world over time reveals a fascinating narrative of resilience and adaptation. The dance of tectonic plates beneath our feet has created mountain ranges, valleys, and oceans, while glaciers, once vast and powerful, have left their indelible mark on the earth's surface. As we delve into this topic, we will explore the intricate relationship between continental drift and glacial activity and uncover the lasting effects on our environment.
The interplay between these two forces is not merely a scientific curiosity; it holds vital implications for our understanding of climate change and the future of our planet. Glaciers that once dominated the landscape have receded, revealing the scars they left behind. As we investigate these changes, we will also consider how they have shaped human history and the implications for future generations. The story of the earth is not just a tale of rocks and ice; it is a narrative woven into the very fabric of life itself.
As we embark on this journey to examine how continents and glaciers have impacted our world, we will raise critical questions about the past, present, and future. From the origins of glacial formations to the role of continental drift in shaping our environments, the answers will illuminate the intricate connections between the earth's geological history and our own existence. Join us as we uncover the mysteries of the planet we call home, focusing on the profound impact of the movement of the continents over time and the glaciers that once dominated the earth.
What Are the Mechanisms Behind Continental Drift?
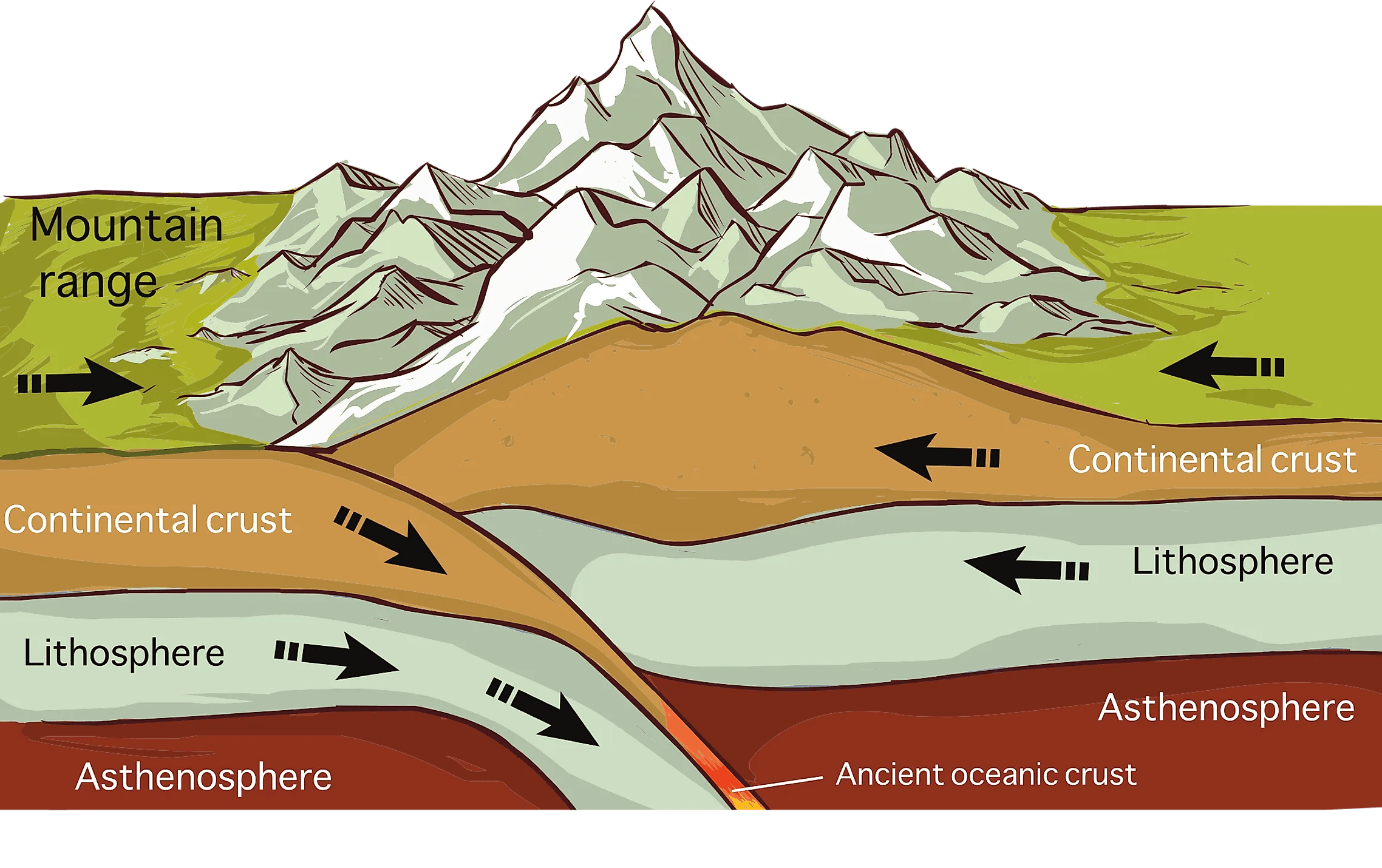
The theory of continental drift, first proposed by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century, explains how continents are not static but rather move over geological time due to tectonic forces. This movement is driven by several mechanisms:
- Plate Tectonics: The Earth's lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath. The interactions between these plates can cause them to collide, separate, or slide past each other.
- Seafloor Spreading: At mid-ocean ridges, new oceanic crust is formed, pushing older crust away and causing continents to drift apart.
- Subduction Zones: These areas are where one tectonic plate is forced under another, leading to the recycling of crust and significant geological activity.
How Did Glaciers Influence the Landscape?
Glaciers that once blanketed significant portions of the Earth have played a crucial role in shaping the landscape. Their immense weight and slow movement have led to various geological phenomena:
- Erosion: Glaciers carve out valleys and shape mountains through processes of erosion, transporting vast amounts of sediment.
- Deposition: As glaciers melt, they leave behind moraines, drumlins, and other landforms that alter the terrain.
- Climate Regulation: Glaciers act as natural climate regulators, reflecting sunlight and influencing local weather patterns.
What Evidence Do We Have of Past Glaciers?
To understand the impact of glaciers that once covered large areas, scientists study various types of evidence:
- Fossil Records: Fossils of plants and animals found in glacial deposits provide insights into ancient ecosystems.
- Geological Features: Features like U-shaped valleys and fjords are clear indicators of glacial activity.
- Ice Cores: Analyzing ice cores from glaciers reveals historical climate data, including atmospheric composition and temperature fluctuations.
How Have Human Activities Influenced Glacial Retreat?
In recent decades, human activities have accelerated the retreat of glaciers, raising concerns over climate change. Some key factors include:
- Global Warming: Increased greenhouse gas emissions have led to rising global temperatures, causing glaciers to melt at an unprecedented rate.
- Land Use Changes: Urbanization and deforestation contribute to changes in local climates, further impacting glacial health.
- Pollution: Black carbon and other pollutants can darken ice surfaces, increasing absorption of heat and accelerating melting.
What Are the Implications of Glacial Retreat?
The consequences of the rapid retreat of glaciers are far-reaching:
- Sea Level Rise: Melting glaciers contribute significantly to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities.
- Water Resources: Many regions rely on glacial meltwater for drinking and agriculture, creating concerns about future water shortages.
- Biodiversity Loss: Changes in habitat due to glacial retreat can lead to the extinction of species reliant on cold environments.
How Can We Mitigate the Effects of Climate Change on Glaciers?
To combat the adverse effects of climate change on glaciers, various strategies can be employed:
- Reducing Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources can help lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting vulnerable ecosystems and promoting sustainable land use practices can aid in preserving glacial environments.
- Public Awareness: Educating communities about climate change and its impacts encourages collective action to mitigate its effects.
How Do We Prepare for a Future Without Glaciers?
The potential loss of glaciers raises critical questions about how societies will adapt:
- Infrastructure Planning: Cities must develop strategies to cope with rising sea levels and altered water supplies.
- Water Management: Developing alternative water sources and efficient usage practices will be essential in areas dependent on glacial melt.
- Climate Resilience: Building resilient ecosystems and communities can help mitigate the effects of climate change and support recovery efforts.
In conclusion, the planet’s geological history is a testament to the impact of the movement of the continents over time and the glaciers that once dominated vast areas. Understanding this interplay allows us to appreciate the delicate balance of our environment and the urgent need to protect it. As we continue to explore the complexities of glaciers and continental drift, we must also commit to safeguarding the future of our planet for generations to come.


ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6ipKmZk6mypXnBsmStoJViurDCxKacp6xdpLNuwMeeZJynnqm2r7HNrapmp6aav27AyKacoKSRmLamvtJmq6GZpGK8r6%2FEZ5%2BtpZw%3D